Mar 22, 2012
Army will fold planned high-security lab into another project
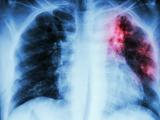
Instead of building a high-containment lab for animal research as a separate structure, the US Army will put it in another facility that's already under construction at Fort Detrick in Frederick, Md., the Frederick News Post reported yesterday. Army officials said a new study showed that demand for the facility, called the Medical Countermeasures Test and Evaluation Center, wasn't high enough to justify a separate building. The facility's purpose is to help speed Food and Drug Administration approval of biodefense drugs and vaccines, the story said. The center's mission will not change, but it will be transferred from the Army Medical Materiel Development Activity (USAMMDA) to the Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID), which is already building new labs at Fort Detrick, with completion expected in 2014, said USAMMDA program manager Kathleen Berst. The report said the lab was announced in 2010 as the answer to a backlog of FDA applications related to disease like Ebola and Marburg fever, for which countermeasures can't be tested in humans. The project had a construction price tag of about $600 million. Berst estimated that scrapping construction would save about $1 billion over the next decade. Last September the National Research Council (NRC) found fault with the Army's risk-assessment plan for the facility.
Mar 22 News Post report
Sep 28, 2011, CIDRAP News story on NRC report
US military awards contract for further development of flu drug
The US Department of Defense (DoD) recently awarded Boston firm MediVector Inc. a $138.5 million contract for further development of the investigational influenza drug favipiravir, also called T-705. In announcing the award on Mar 15, DoD's Joint Project Manager Transformational Medical Technologies (JPM-TMT) described the antiviral as "a broad-spectrum therapeutic against multiple influenza viruses." "This drug shows promise that it can mitigate flu symptoms by interfering with the influenza replication process," David E. Hough, joint project manager for JPM-TMT, said in a press release. Favipiravir has already shown positive results in numerous animal studies and in phase 1 clinical trials, the release said. Lt. Col. David Gibson, another JPM-TMT official, said phase 3 clinical trials for the drug could begin as early as this fall. Favipiravir was originally developed by Toyama Chemical Co. of Japan and has a different mechanism of action from neuraminidase inhibitors, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu), according to earlier reports.
Mar 15 JPM TMT news release
Oct 29, 2009, CIDRAP News story that mentions T-705 clinical trials
US TB rate reached all-time low in 2011, but disparities increased
The incidence of new tuberculosis (TB) cases in the United States dropped to an all-time low in 2011, but disparities among racial and ethnic groups and between US- and foreign-born Americans grew, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported today. The nation had 10,521 new TB cases in 2011, or 3.4 cases per 100,000 population, which is 6.4% lower than the rate in 2010 and the lowest since national reporting began in 1953, the CDC said in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR). But compared with figures for whites, TB rates were seven times higher in Hispanics, eight times higher in blacks, and 25 times higher in Asians. Although cases have declined even among Asians, they have become the largest ethnic group among TB patients, with 29.9% of all cases. Further, the TB rate for foreign-born people was 12 times that of those born in the United States. In other findings, 81% of TB patients had a known (positive or negative) HIV status, and 7.9% had the co-infection, an all-time low. A total of 109 cases of multidrug-resistant TB were reported in 2010, the latest figures available, and four cases of extensively drug-resistant disease were reported in 2011. Noting that the TB rate still falls short of the goal of 1.0 case per 100,000, set in 1989, the CDC said, "If current efforts are not improved or expanded, TB elimination is unlikely before the year 2100."
Mar 23 MMWR article
Unique triple reassortant H3N2 viruses in turkeys include pH1N1 genetic material
Three unique triple reassortant (TR) H3N2 influenza viruses bearing gene segments from 2009 pandemic H1N1 (pH1N1) in domestic turkeys were reported by a Canadian group in PLoS One yesterday. To the authors' knowledge, this is the first time pH1N1/TR H3N2 reassortant viruses have been reported in domestic poultry. Tracheal and cloacal swabs were obtained from turkeys on three geographically separate breeder turkey farms in southern Ontario that had experienced significant drops in egg production but no clinical signs of disease. Genetic characterization of the samples from one farm showed the eight gene segments of the virus to all be of TR H3N2 lineage. The samples from the other two farms, however, were unique reassortants, with gene segments from both pH1N1 and TR H3N2. The turkeys on the latter two farms had been vaccinated before the outbreak with the only vaccine approved in Canada against H3N2 influenza in turkeys, an H3N4 oil emulsion vaccine. The researchers found that sera collected from the vaccinated turkeys were not able to neutralize the new pH1N1/TR H3N2 virus isolated in the study. The authors note that close proximity of turkey and swine farms, which is thought to play a role in the epidemiology of TR H3N2 flu virus infection in turkeys, is common in the area where the tested farms are located. They also say that, despite the common view of pigs as efficient "mixing vessels" for generations of reassortant influenza viruses, "We cannot exclude the possibility that the reassortment between TR H3N2 and pH1N1 took place in turkeys."
Mar 21 PLoS One article
Measles cases down in much of Europe, Ukraine not included
January of this year saw 584 cases of measles reported by 29 European Union and European Economic Area countries, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) announced today. This number is far lower than the numbers in January of 2011 and 2010, which stood at 2,289 and 2,673, respectively. No new measles cases were reported from 15 of the countries, and the only country with more than 1 case per 100,000 population was Romania. Of concern is an outgoing outbreak of measles in Ukraine, particularly the western part of the country, which borders on Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. Ukraine, along with Poland, is hosting the European Football Championship (Euro 2012) in June, expected to attract numerous soccer fans. Elimination of measles by 2015 is the stated goal of the World Health Organization's European Region countries, which includes the 29 countries reporting here.
Mar 22 ECDC press release