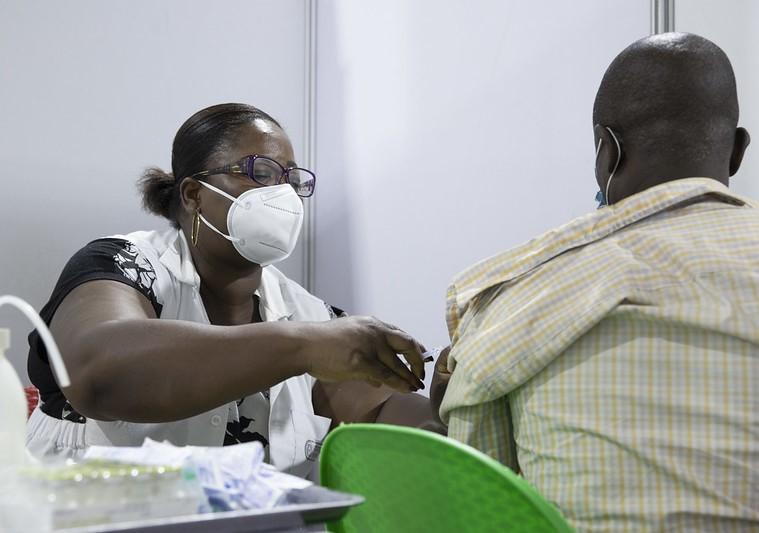
Americans living in rural areas are less likely to be vaccinated against COVID-19 than their urban counterparts, and the gap between the two groups did not close during the Delta and Omicron surges, according to research published today in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR).
The study was based on county-level vaccine administration data among persons aged 5 years and older who received their first dose of either the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 vaccine, or a single dose of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine, from Dec 14, 2020, through Jan 31, 2022.
In rural counties, the rate of first dose vaccine uptake was 58.5%, compared to 75.4% in urban counties. Those percentages stayed consistent throughout the pandemic, despite surges of virus activity caused by new variants.
"Among all age groups, vaccination coverage with ≥1 doses was lower in rural counties, with the largest absolute difference (26.2 percentage points) among those aged 12–17 years (38.7% rural, 64.9% urban) and the largest relative difference among those aged 5–11 years (14.7% rural, 30.5% urban)," the authors said.
The authors said the disparity can be linked to a lack of access to health care, and, notably, found that nearly 40% of rural parents reported that their child's pediatrician did not recommend a COVID-19 vaccine, compared with only 8% of parents in urban communities.
Overall, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) COVID Data Tracker shows that 65% of Americans are fully vaccinated against COVID-19, 76.4% have received at least one dose of vaccine, and 43.8% of fully vaccinated Americans have received a booster dose.
New Orleans lifts mask mandates as cases drop
As cases continue to decline around the country, New Orleans this morning became the latest major city to announce it has lifted its indoor mask mandate, the Associated Press reports. The requirement that customers show proof of vaccination or a recent negative test at restaurants, bars, and other indoor venues will end on Mar 21.
The United States reported 52,355 new COVID-19 cases yesterday, and 2,095 deaths, according to the Johns Hopkins COVID-19 tracker.
The 7-day average of new daily cases is 54,734, with 1,838 daily deaths, according to the New York Times tracker.
The Department of Health and Human Services Protect Public Data Hub shows 41,014 inpatient beds in use for COVID-19.
Long COVID, pandemic misinformation
- Sen. Tim Kaine of Virginia, who is still experiencing mild COVID-19 symptoms nearly 2 years after getting infected, is among the sponsors of a bill to fund research into the long-term effects of the disease, the Washington Post reported yesterday.
- The US Surgeon General has formally requested that the major tech platforms submit information about COVID-19 misinformation on social networks, search engines, crowdsourced platforms, e-commerce sites, and instant messaging systems, according to the New York Times.