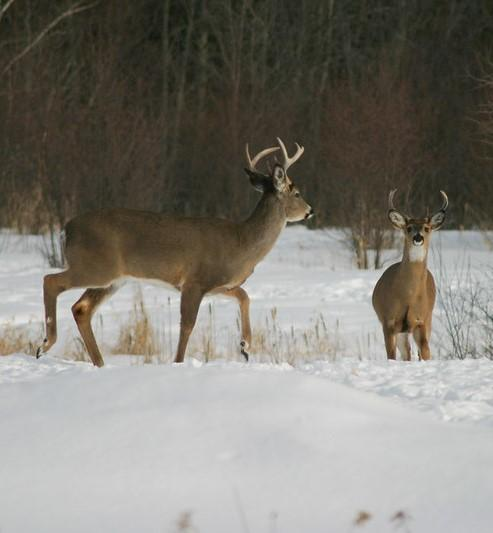
Yesterday in Clinical Infectious Diseases, scientists report on four people in Michigan who contracted tuberculosis (TB) linked to wild deer and domestic cattle from 2019 to 2022, raising the total number of zoonotic cases in the state to seven since 2002.
A team led by physicians at Corewell Health East and the University of Michigan reviewed data and Mycobacterium bovis cultures from the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services TB database. They conducted interviews and compared whole-genome sequences of human isolates with a veterinary library of M bovis strains.
The study authors noted the 1994 identification of M bovis cases in wild deer in northern lower Michigan in 1994, with transmission to local cattle. From 2002 to 2017, M bovis infections in three deer hunters were reported in the state.
Continued spread among humans, animals
The three confirmed and one probable human M bovis cases identified from 2019 and 2022 resulted in cutaneous disease, two cases of severe pulmonary disease, and one case of human-to-human spread. Those infected were a taxidermist, a woman who interacted with deer in the affected area, and a man with no obvious animal exposures and his female household contact. The three human isolates had zero to three mutations linked to M bovis strains circulating in local deer and cattle.
Future studies should examine the routes of transmission and degree of risk to humans through expanded epidemiological surveys.
The authors said M bovis continues to spread from deer to humans and cattle and poses a particular risk to people with weakened immune systems.
"Future studies should examine the routes of transmission and degree of risk to humans through expanded epidemiological surveys," they wrote. "A One Health approach linking human, veterinary, and environmental health should address screening for TB infection, public education, and mitigation of transmission."
M bovis is usually tied to TB in cattle, which can transmit the bacteria to humans through consumption of unpasteurized dairy products. The bacteria cause disease that is indistinguishable from that caused by M tuberculosis, and common diagnostic tests can't identify M bovis, the authors said.