Vaccination against herpes zoster (shingles) may reduce the risk of heart disease, dementia, and death in adults aged 50 and older, according to Case Western University research presented yesterday at IDWeek 2025 in Atlanta.
For the matched cohort study, the researchers analyzed electronic health record data from more than 174,000 patients at 107 US health systems. Follow-up was 3 months to 7 years after vaccination. The study has yet to be published in a peer-reviewed journal.
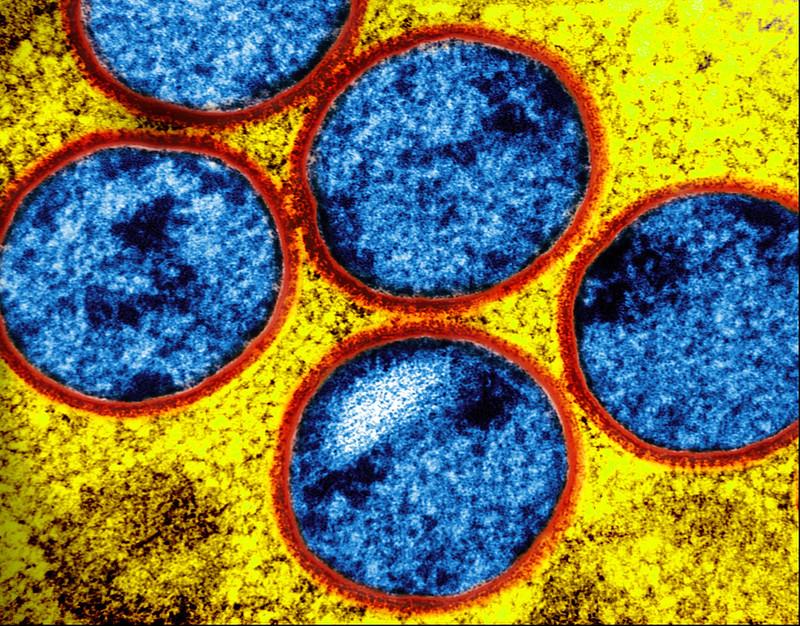
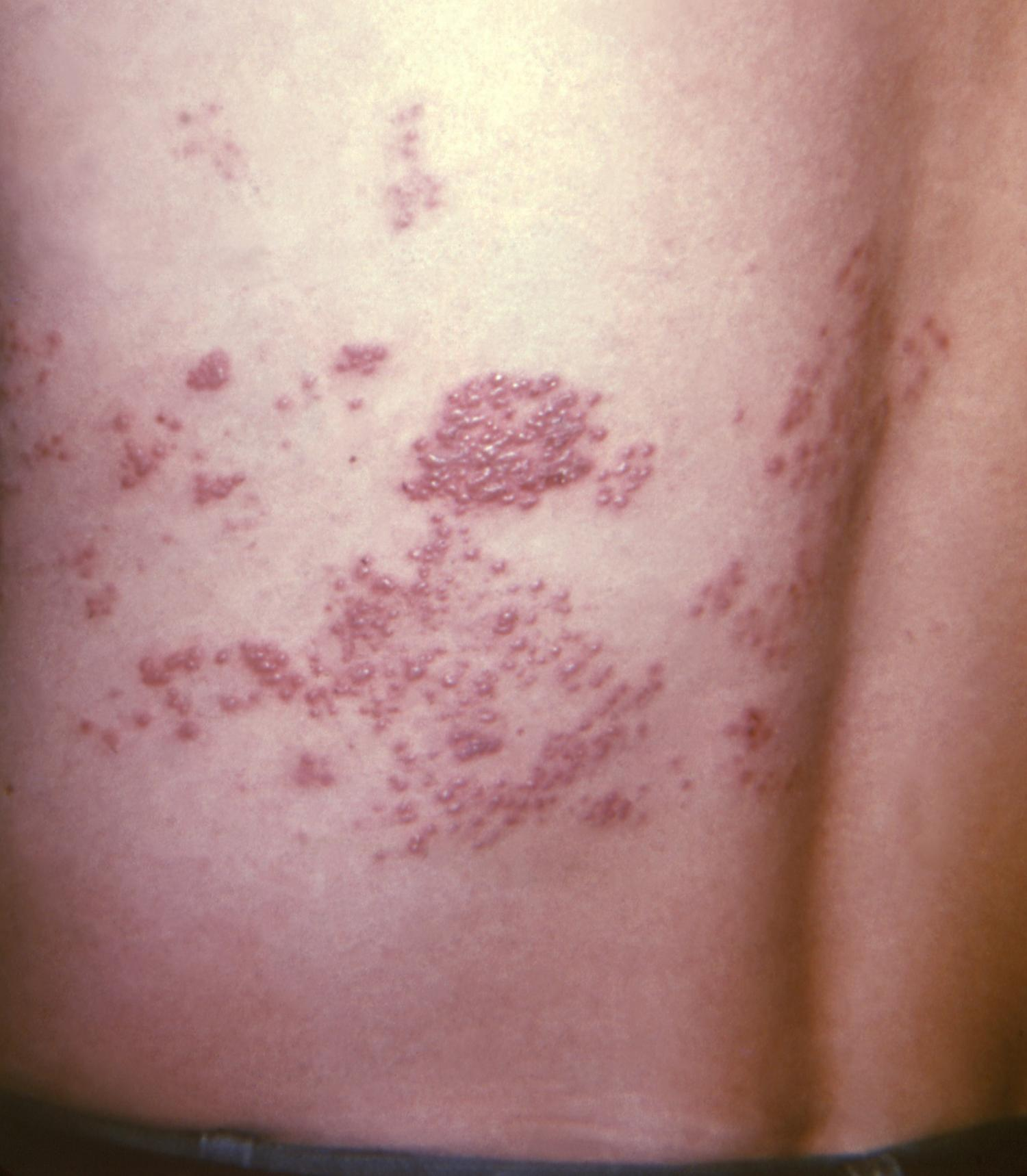
Caused by reactivation of the varicella-zoster (chickenpox) virus, shingles causes a painful, itchy rash that follows a nerve, often accompanied by fever, headache, fatigue, and light sensitivity.
While the infection isn't life-threatening, it can lead to postherpetic neuralgia (long-term shingles pain), neurologic conditions, skin infections, and vision loss. Older people are at higher risk for shingles and its complications.
Vaccination with the Shingrix vaccine, approved in 2017, is recommended for people aged 50 years and older, regardless of shingles history or previous receipt of the now-discontinued Zostavax vaccine.
Potential 50% reduction in vascular dementia
Relative to pneumococcal vaccination, shingles vaccination was tied to a lower risk of vascular dementia (50%), blood clots (27%), heart attack or stroke (25%), and death (21%). The study authors said that the findings suggest that the shingles vaccine can prevent both infection and its complications.