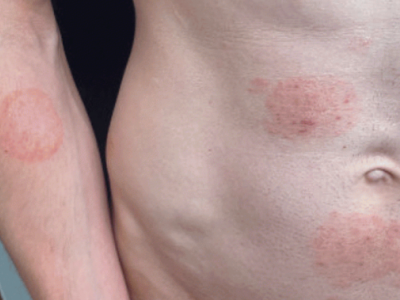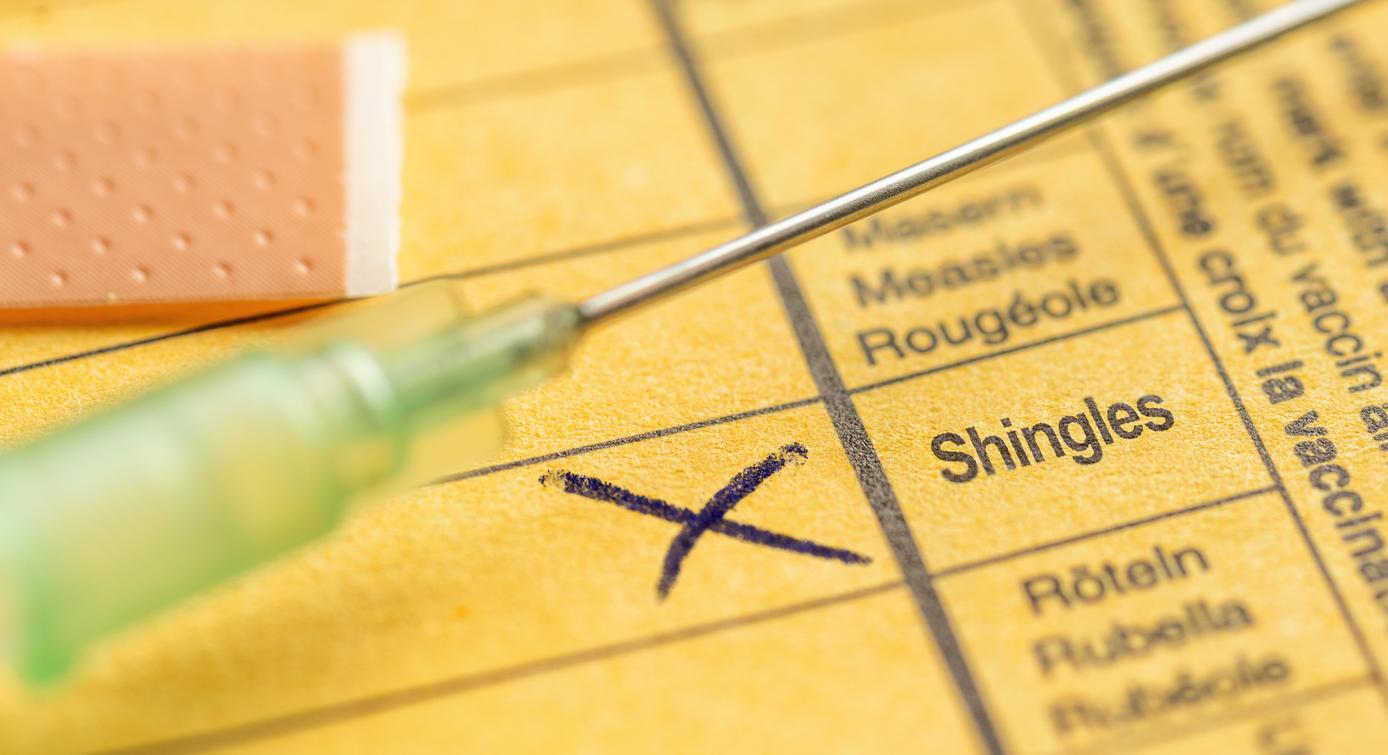
A new global systematic literature review and meta-analysis shows that shingles vaccination is associated with a statistically significant lower risk of heart attack and stroke, according to a study presented today at the 2025 European Society of Cardiology Congress.
The study is based on 19 studies, and the final analysis included eight observational studies and one randomized controlled trial. Across all nine studies, 53.3% of participants were male.
Overall, any herpes zoster (HZ; shingles) vaccination was associated with a significantly lower risk of stroke and heart attack versus no HZ vaccination. Among adults ages 18 to 49 and those 50 and older, vaccine effectiveness was 18% (95% confidence interval [CI], 13% to 24%) and 16% (95% CI, 13% to 18%) in preventing cardiovascular events, respectively.
More studies need to prove causality
In studies that calculated cardiovascular event absolute risk, the absolute rate difference ranged from 1.2 to 2.2 fewer events per 1,000 person-years among all vaccinated adults.
Further research studies are now needed to find out whether this association can be attributed to an effect of herpes zoster vaccination.
Charles Williams, global associate medical director, Global Medical Affairs–Vaccines at vaccine manufacturer GSK, said in a press release, “In this analysis, vaccination against herpes zoster was associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks or strokes. Further research studies are now needed to find out whether this association can be attributed to an effect of herpes zoster vaccination.”
Williams said almost all studies included in the analysis were observational and can't be used to infer causality.