Report details farm findings in 2011 cantaloupe Listeria outbreak
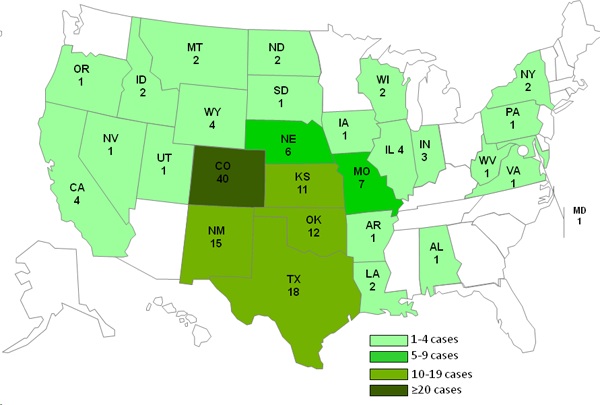
Newly installed used cleaning equipment likely played a significant role in the 2011 outbreak of listeriosis linked to Colorado cantaloupe that sickened 147 (see CDC map below) and killed 33, according to a report in today's New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM).
Scientists from the US Centers for the Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and elsewhere provided details on the investigation of the outbreak, which ran from Aug 1 to Oct 31, 2011, and affected 28 states.
The implicated farm is called "Farm A" in today's report but was previously named by the CDC as Jensen Farms of Granada, Colo., in the Rocky Ford growing region in the southeastern part of the state. The farm had previously used recirculating chlorinated, chilled water to clean and cool cantaloupes.
In 2011, however, the farm installed washing and drying equipment that was previously used for packing "another raw agricultural commodity," the NEJM report said. Jensen's new system used municipal water that wasn't recirculated and didn't have added chlorine.
Of 39 environmental swabs taken from food-contact or adjacent surfaces on Jensen Farms, 12 yielded Listeria monocytogenes isolates matching the outbreak strain. All 12 swabs were collected either within or "immediately downstream" from the newly installed equipment, the report said.
"The findings of our investigation indicate that cantaloupe contamination most likely occurred during processing operations conducted by Farm A," the authors concluded, adding that the new washing and drying process probably promoted bacterial growth.
Sep 5 NEJM abstract
Aug 27, 2012, final CDC update on the outbreak
CDC: Recent waterborne outbreaks caused 1,000+ illnesses
Waterborne disease outbreaks in 2009 and 2010 caused 1,040 illnesses, 85 hospitalizations, and 8 deaths, with Legionella for the first time accounting for more than half the outbreaks, the CDC reported today in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR).
Using data from the Waterborne Disease and Outbreak Surveillance System, CDC researchers reported 33 outbreaks related to contaminated drinking water, which was about the same as in 2007-08, when 36 such outbreaks occurred.
Legionella accounted for 58% of outbreaks and 7% of illnesses, they reported, and Campylobacter accounted for 12% of outbreaks but 78% of illnesses. The most commonly identified cause in these outbreaks was Legionella in plumbing systems (57.6%), followed by untreated groundwater (24.2%) and deficiencies in water distribution systems (12.1%).
They also reported 12 outbreaks associated with other nonrecreational water use that caused 234 illnesses, 51 hospitalizations, and 6 deaths. Legionella accounted for 58% of these outbreaks, as well as 42% of cases, 96% of hospitalizations, and all deaths.
An editorial note with the report said, "Legionella outbreaks are particularly challenging to prevent and control, in part because the organism multiplies in plumbing systems within buildings, which usually fall outside of regulatory oversight."
The note also called for full implementation of the federal Ground Water Rule to address improperly treated groundwater.
Sep 6 MMWR report













