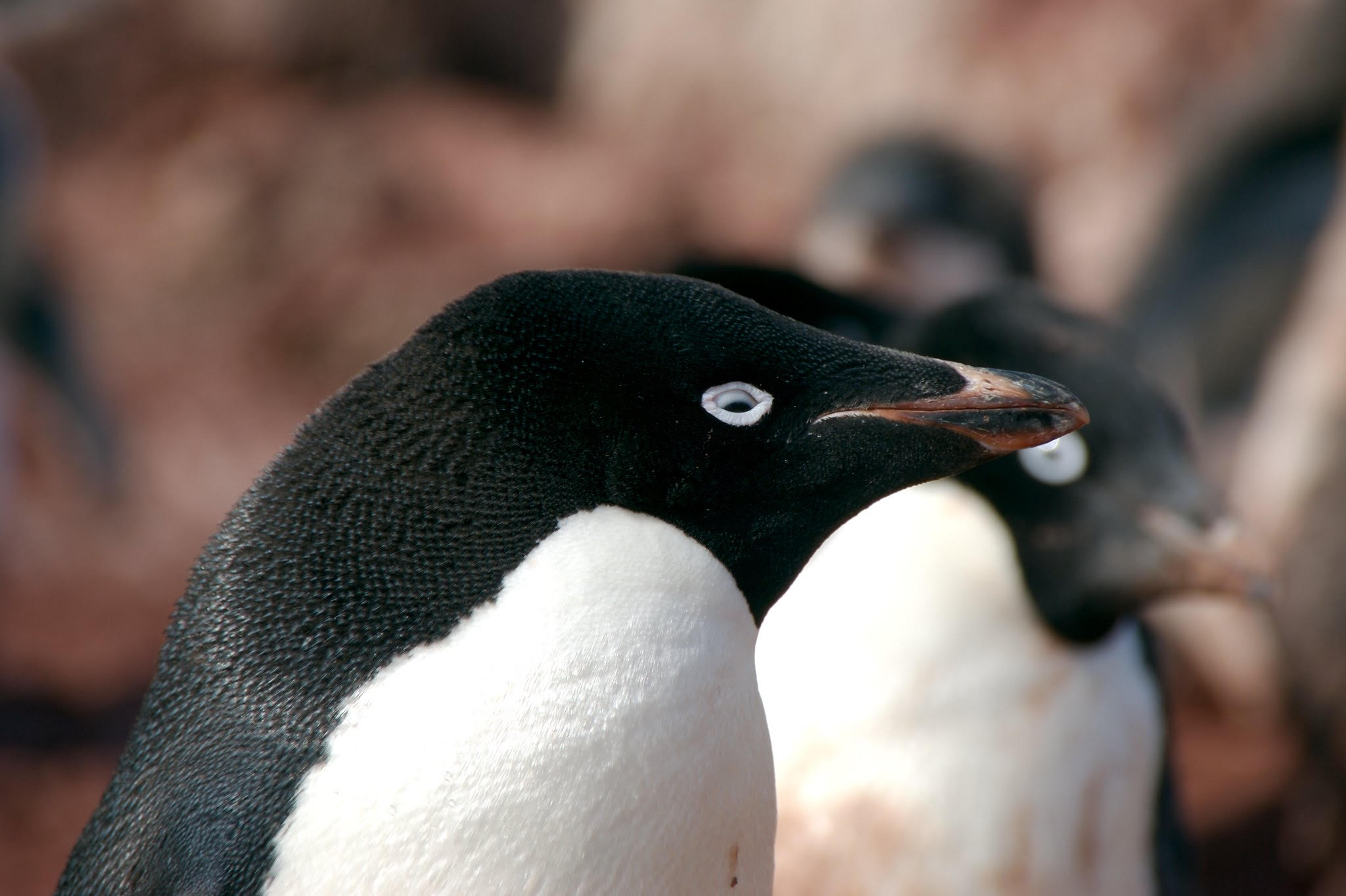
In Scientific Reports today, Chilean researchers describe the first-time detection of suspected H5 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (HPAIV) in penguins and cormorants in Antarctica, which they say could indicate a significant expansion of the virus into the continent that would put susceptible bird species at risk.
The team conducted a geographic survey of seabirds at 13 breeding sites ranging from the northeastern Antarctic Peninsula to the Ross Sea, including the coasts of the Bellinghausen and Amundsen seas, in December 2023 and January 2024.
Beginning in 2020, clade 2.3.4.4b avian flu rapidly spread across continents, mainly driven by wild bird movements. "In Chile, it was detected for the first time in October 2022," the investigators wrote. "Given its close proximity to the Antarctic continent and the migratory movements of birds between both regions, transmission is highly likely, causing a significant threat to the Antarctic wildlife."
No clinical signs of avian flu
Of the 115 birds sampled, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test results for 9, including 8 Adelie penguins (12%) at 2 different locations and 1 Atlantic cormorant, were suspected positive for H5 avian flu. Nearly all suspected infections were from Beagle Island, close to the Danger Islands at the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. Another infected penguin was identified on the West Antarctic Peninsula, south of the Antarctic Circle in Margaret Bay.
This study suggests the possibility of the first cases of HPAIV H5 in the Antarctic continent, potentially adding two new species to the list of infected species.
None of the birds sampled showed clinical signs of influenza infection, and the seven penguins with suspected infection on Beagle Island were still foraging as of March 2024, more than 2 months after testing.
"This study suggests the possibility of the first cases of HPAIV H5 in the Antarctic continent, potentially adding two new species to the list of infected species," the study authors wrote. "It also highlights the southernmost suspected cases identified to date of surveillance, and notably, no cases were detected between the Antarctic Peninsula and the Ross Sea."
.jpg)
-2.jpg)